LCD (LED) TV Main Control Unit
Although commonly referred to as "LED TVs," they are technically LCD TVs that utilize LED backlighting. The core brain and central nervous system of this TV is its Main Control Board, also known as the Main Board, Motherboard, or Signal Board. It is responsible for converting raw data from various signal sources into the stunning images we see and the powerful sound we hear. Below, we will conduct an in-depth analysis from five aspects: components, electronic elements, function and principle, development trends, and market.
Components of the Main Control Board
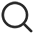
The main control board is a highly integrated multi-layer printed circuit board (PCB) populated with numerous core chips and peripheral circuits. Divided from a functional module perspective, it consists of the following core parts:
1. Main Processor (SoC - System on Chip) Unit: This is the absolute core of the mainboard, equivalent to the TV's "brain." It is typically a highly integrated System-on-Chip (SoC) containing a Central Processing Unit (CPU), Graphics Processing Unit (GPU), Video Processing Unit (VPU), Audio Processing Unit (APU), and various controller interfaces.
2. Memory Unit:
- DRAM (Dynamic Random-Access Memory): Serves as the system's running memory (RAM), used for temporarily storing the operating system, applications, and data being processed. Its capacity directly affects the TV's operational smoothness and multitasking capability.
- Flash Memory: Serves as the storage memory (ROM), used for permanently storing the TV's firmware, operating system (e.g., Android TV, webOS), applications, and user settings.
3. Power Management Unit (PMU): Responsible for the secondary conversion and distribution of direct current (DC) received from the power supply board (e.g., 12V, 5V, 3.3V). It provides the required different voltages and currents for various chips and circuits on the mainboard, ensuring their stable and efficient operation.
4. Input/Output (I/O) Interface Unit: This is the physical gateway for the TV to connect to external devices, including:
- HDMI Interfaces: Receive high-definition digital audio and video signals from devices like Blu-ray players, game consoles, and computers.
- USB Interfaces: Connect USB flash drives, external hard drives for media playback or firmware updates.
- Antenna/RF Interface: Receives terrestrial or cable TV signals.
- AV Input/Output Interfaces: Provide compatibility for legacy devices (e.g., DVD players).
- Optical Audio Output (S/PDIF): Outputs high-quality digital audio to soundbars or amplifiers.
- Ethernet (LAN) Port and Wi-Fi/BT Module: Provide wired and wireless network connectivity.
- RF Bluetooth/Voice Module Interface: Used for connecting the remote control, supporting Bluetooth and voice functions.
5. Signal Processing and Transmission Unit:
- T-CON (Timing Controller) Interface: Transmits processed image signals and timing control signals to the T-Con board via LVDS (Low-Voltage Differential Signaling) or more advanced interfaces like eDP or V-by-One®, ultimately driving the LCD panel display.
- Backlight Control Circuit: Outputs PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signals to control the brightness and switching of the LED backlight unit, enabling dimming functions (e.g., global dimming, local dimming).
- Audio Amplifier Circuit: Amplifies the processed audio signal to drive the TV's built-in speakers.
Key Electronic Components Used
The mainboard aggregates various electronic components, from simple to complex, primarily including:
Integrated Circuits (ICs):
- Main Chip (SoC): Solutions from brands like MediaTek, Amlogic, HiSilicon.
- Memory Chips: DRAM chips (from Samsung, SK Hynix, Micron), NAND Flash chips (from Samsung, Kioxia (Toshiba), Western Digital (SanDisk)).
- Power Management ICs (PMICs): Products from brands like Texas Instruments (TI), Infineon.
- Audio Codec Chip and Audio Amplifier Chip.
- Ethernet Controller Chip and USB Hub Controller Chip.
Passive Components:
- Resistors: Used for current limiting, voltage division, pull-up/pull-down.
- Capacitors: Used for filtering, decoupling, energy storage, coupling. Extensive use of Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCCs) and electrolytic capacitors.
- Inductors: Form LC filter circuits with capacitors, used for power conversion and voltage stabilization.
Connectors and Headers: Physical sockets for all external interfaces (HDMI, USB, etc.).
Crystal Oscillators: Provide the system's reference clock signal, the "heartbeat" for chip operation.
Transistors and Diodes: Used for circuit switching, signal amplification, and power protection.
PCB (Printed Circuit Board): Typically a 6 to 8-layer or more multi-layer board, providing electrical connections and mechanical support for all components.
Detailed Function and Working Principle
The operation of the main control board is a complex signal processing pipeline. Its working principle can be summarized as follows:
1. Signal Reception and Input Selection: When the user selects a signal source (e.g., HDMI 1) via the remote, the main processor controls electronic switches to activate the corresponding input channel.
2. Signal Decoding and Demultiplexing: For received digital signals (e.g., TMDS signals via HDMI), the board first decodes them. If the signal source is compressed (e.g., DTMB digital TV signal, network video stream), the VPU within the SoC decompresses (decodes) it, handling formats like H.264, H.265 (HEVC), AV1, etc. For TV signals, demultiplexing (Demux) is also required to separate the video, audio, and data streams within the transport stream.
3. Image Processing and Enhancement (Core of Picture Quality): This is the crucial step determining picture quality.
- Scaling: Converts input signals of different resolutions (e.g., 1080p, 4K) to the screen's native physical resolution (e.g., 4K). The quality of the algorithm directly impacts the clarity after scaling.
- Noise Reduction (NR): Eliminates noise from the video source, improving picture purity.
- Motion Compensation (MEMC - Motion Estimation, Motion Compensation): Uses algorithms to insert calculated transition frames between original frames, significantly improving the fluidity of motion pictures and reducing blur.
- Color Management: Adjusts color gamut, gamma value, and color accuracy to make colors more vibrant and precise.
- Contrast Enhancement (Local Dimming): The mainboard generates backlight control signals based on the image content and sends them to the backlight driver board. During dark scenes, it dims or turns off the backlight in corresponding areas, significantly enhancing contrast and achieving purer blacks.
4. Audio Processing: The separated audio data is sent to the SoC's APU or an external Codec chip for processing, such as decoding Dolby or DTS audio formats, applying virtual surround sound processing, or equalization adjustments. The processed digital signal can be output directly via optical port or converted to an analog signal by the audio amplifier chip to drive the speakers.
5. Output and Display: The processed video data (in RGB or YUV format) along with line and field synchronization signals are sent to the T-Con board via LVDS or other high-speed serial interfaces. The T-Con board then converts these signals into timing signals that precisely control the alignment of the liquid crystal molecules, delivering them to the source driver and gate driver chips, ultimately forming an image on the screen. Simultaneously, the backlight PWM signal generated by the mainboard controls the brightness of the backlight unit, synchronizing with the image content.
6. System Control and Smart Features: The CPU within the SoC runs the smart operating system (e.g., Android TV), manages the user interface (UI), installs and runs apps, processes network data, responds to voice commands, etc., transforming the TV into a smart entertainment center.
Development Trends
The main control board market is a typical B2B market, mainly composed of upstream chip solution providers and downstream TV manufacturers.
1. Extremization of Picture Quality Processing Technology:
- 8K Ultra High Definition: Support for decoding and displaying 8K at 60Hz or even 120Hz, placing extremely high demands on the SoC's processing power and memory bandwidth.
- More Advanced AI Picture Engines: Utilizing artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms for real-time scene and object recognition, enabling pixel-level optimization of picture content, such as AI-SR (Super Resolution), AI color management, and AI motion compensation.
- Higher Standard HDR: Support for dynamic HDR formats like Dolby Vision and HDR10+, delivering richer highlight and shadow details.
2. Centralization of Smart Interaction and Connectivity:
- Stronger SoC Performance: CPU/GPU performance is approaching mobile platform levels to run complex smart systems and large games smoothly.
- Enhanced Gaming Features: Support for HDMI 2.1 features like ALLM (Auto Low Latency Mode) and VRR (Variable Refresh Rate), making TVs ideal displays for game consoles.
- Whole-Home Smart Hub: TVs are becoming control and display centers for smart homes, enabling interactions like video calls and fitness guidance via far-field voice and cameras.
3. Coexistence of Architectural Integration and Modularization:
- High Integration: To reduce costs, more functions are integrated into the SoC. "Three-in-one boards" that integrate T-Con functionality are common in the low-end market.
- Modular Design: In the high-end market, separated mainboard, power board, and T-Con board designs remain mainstream for ease of upgrade, repair, and pursuit of ultimate performance (e.g., eliminating signal interference). Concepts like "modular upgrade cards" are emerging, allowing upgrades of core TV functions by replacing specific modules.
4. Energy Efficiency and Environmental Protection: New power management chips and design schemes aim to reduce standby and operational power consumption, complying with increasingly stringent global energy efficiency standards.
Market Situation
The main control board market is a typical B2B market, primarily composed of upstream chip solution providers and downstream TV manufacturers.
1. Supply Chain Structure:
- Chip Solution Providers (Dominants): MediaTek holds the absolute leading position in the global smart TV SoC market with its Pentonic series chips. Their solutions are widely used by numerous brands like Samsung, Sony, Hisense, and TCL. Amlogic and Realtek hold shares in parts of the mid-to-low-end market and specific brands. HiSilicon was once a major player.
- TV brand manufacturers such as Samsung LG、 Sony TCL、 Hisense, Xiaomi, etc. They either adopt a public version solution or collaborate deeply with chip manufacturers for customization (such as Sony's X1/XR graphics chip, which is deeply optimized based on the MediaTek platform).
- Third-party Mainboard Suppliers: A large third-party repair market exists, providing replacement mainboards for various TV models.
2. Market Competition Focus:
- Technology Race: The core competition lies in picture quality algorithms, AI capabilities, gaming performance, and support for decoding formats (e.g., AV1). Those who can provide superior comprehensive experiences win orders from top brands.
- Cost Control: In the mid-to-low-end market, cost is the decisive factor. Solution providers need to offer highly cost-effective solutions through high integration and economies of scale.
- Customization Services: Major brands seek differentiated solutions. Therefore, chip solution providers need to offer flexible hardware and software customization services to help brands establish unique picture quality and user experience characteristics.
3. Future Market Drivers:
- Replacement Demand: The upgrade cycle from 1080p to 4K is largely complete. Future adoption of 8K, Mini LED, and other new technologies will be the main driver for growth in the high-end market.
- Emerging Technologies: New display technologies like transparent displays, laser TVs, and Micro LED may create new demand for main control boards.
- Emerging Markets: In some developing countries, space remains for first-time purchases and CRT TV replacements.
In summary, the main control board of an LCD (LED) TV is a highly complex conductor, orchestrating every step from signal input to final display. It not only determines the TV's basic functions but is also the ultimate arbiter of picture quality, sound quality, and smart experience. Its technology is rapidly developing towards greater intelligence, clarity, and connectivity. Market competition, led by chip giants, will continue to revolve around technological innovation and cost-effectiveness.
The advantages of SMC
SMC, as a globally leading power semiconductor device manufacturer with nearly 30 years of history, can provide customers with the most advanced, efficient, and cost-effective third-generation silicon carbide MOSFETs and silicon carbide JBS diodes. In addition, SMC has unique experience in silicon-based power diode devices, and its best-selling high-power ultra-fast recovery diodes, high current Schottky diodes, and other products are highly praised by customers worldwide. SMC's power semiconductor devices can provide higher efficiency, better reliability, good delivery time, and competitive prices for your products. SMC's professional service team around the world allows you to experience the ultimate customer service experience and safeguard your product design.












































 点击获赠免费样品!
点击获赠免费样品!